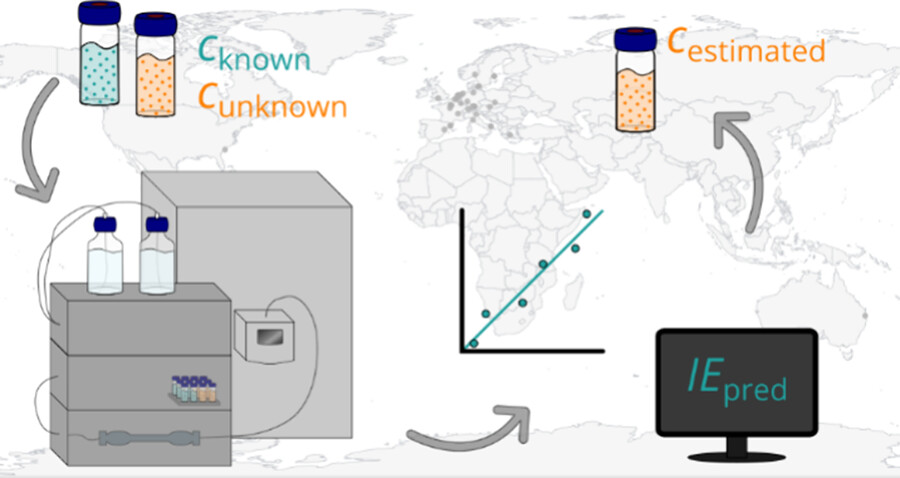
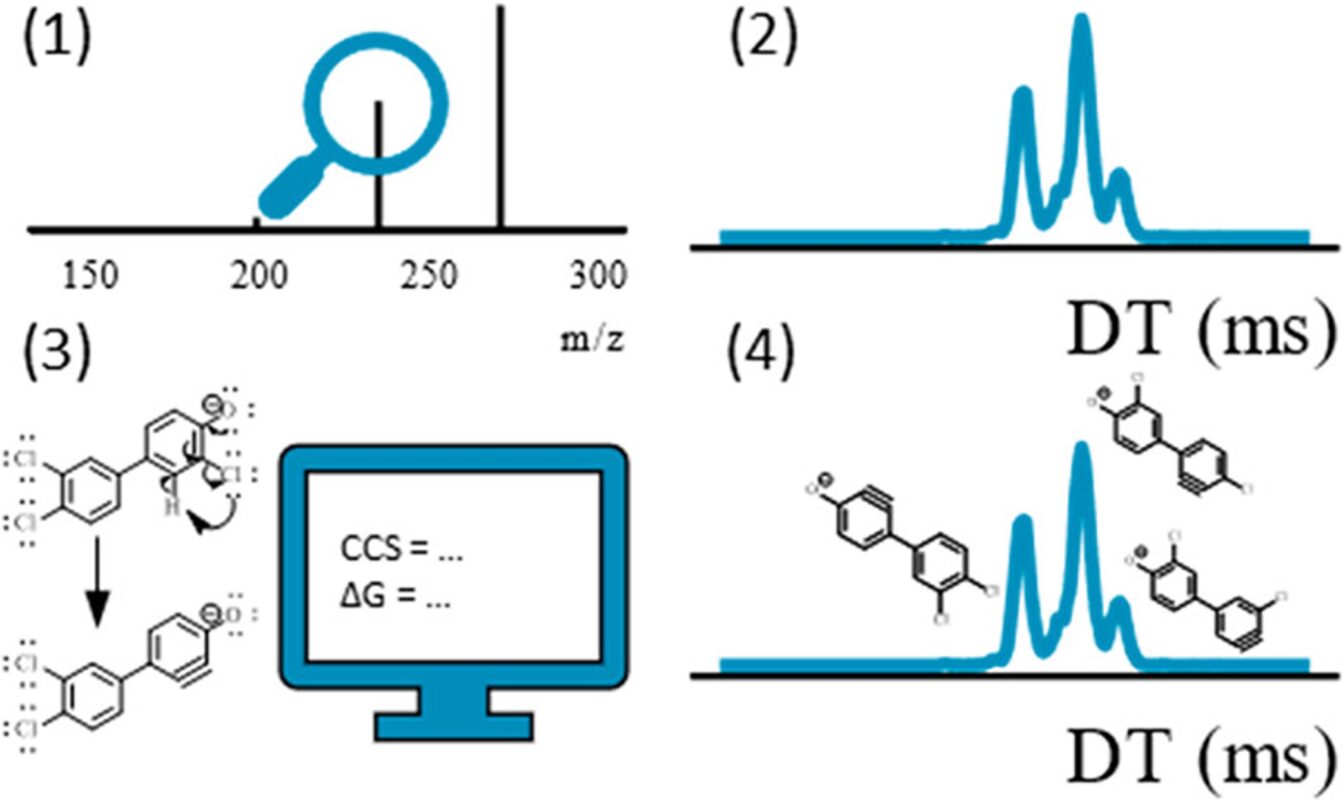
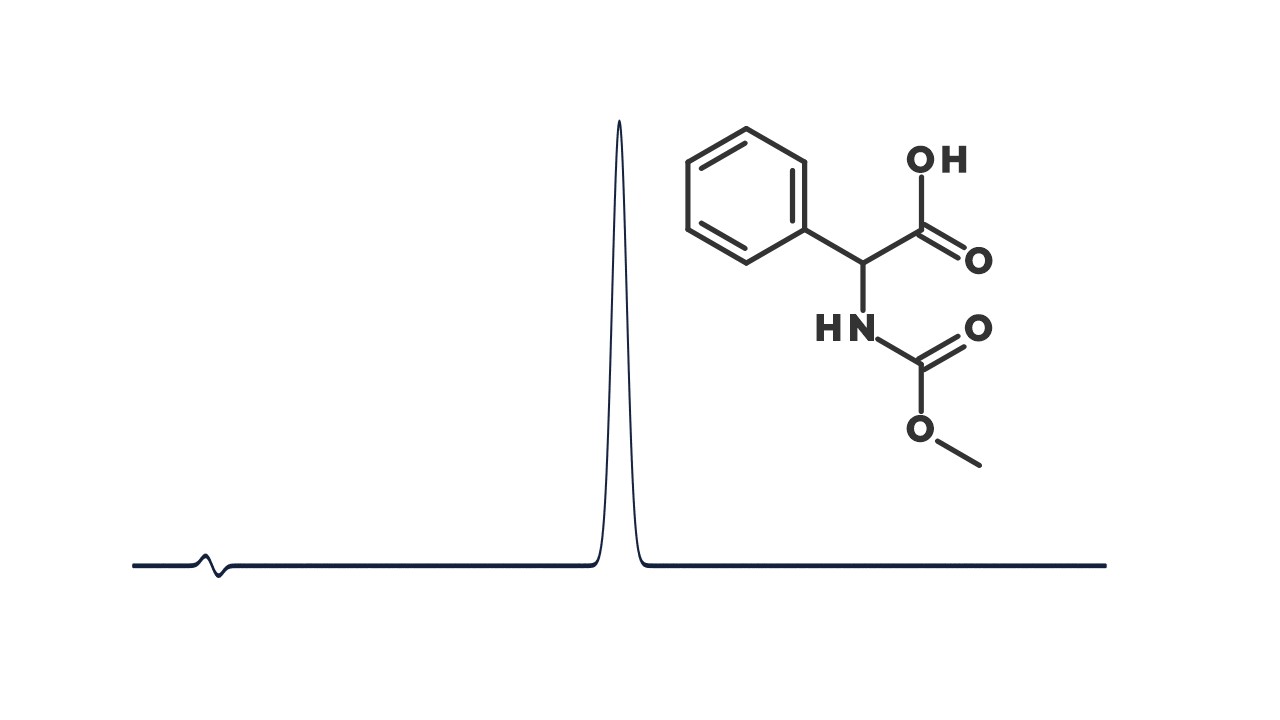
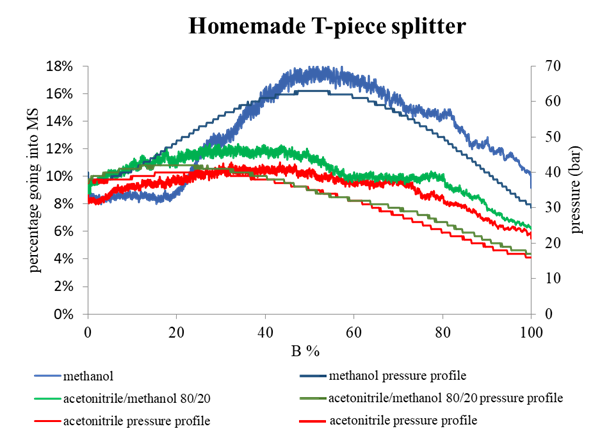
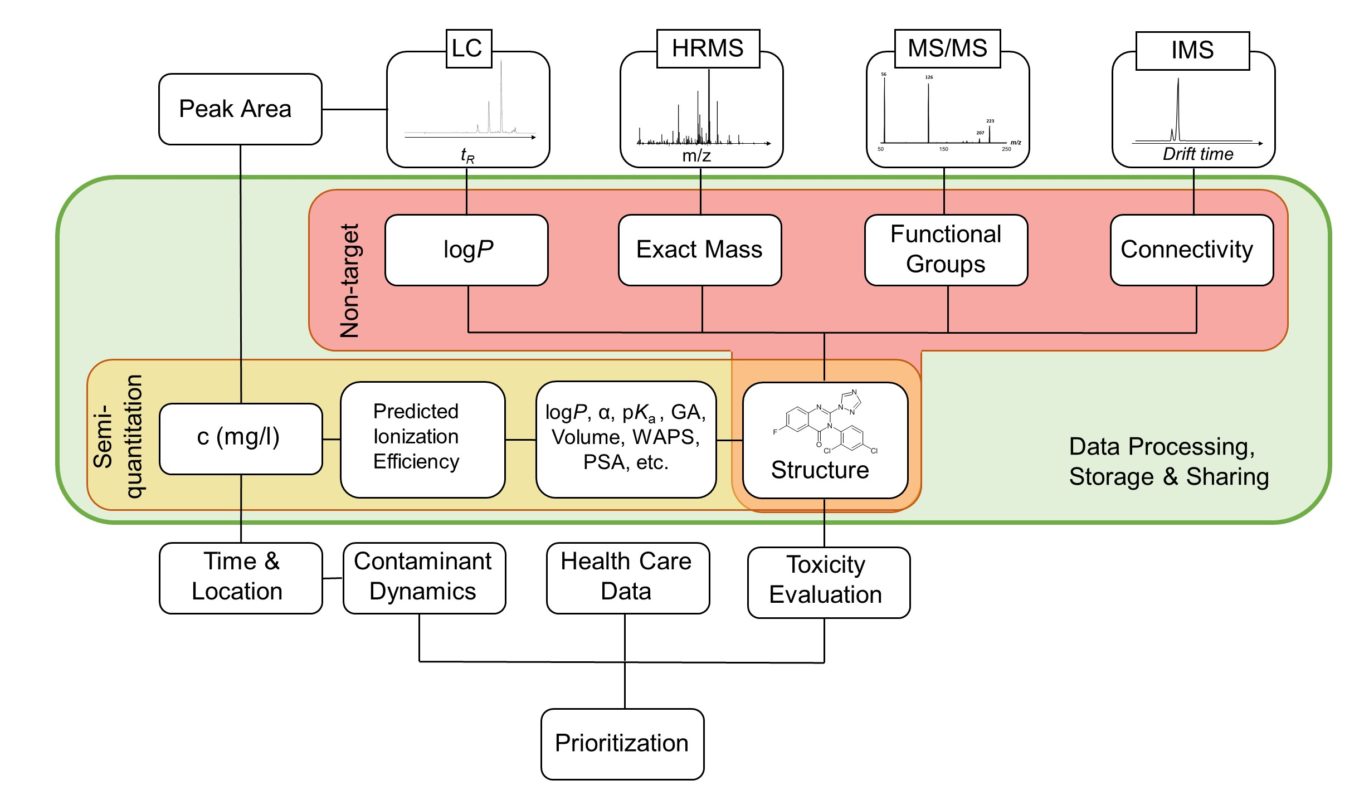
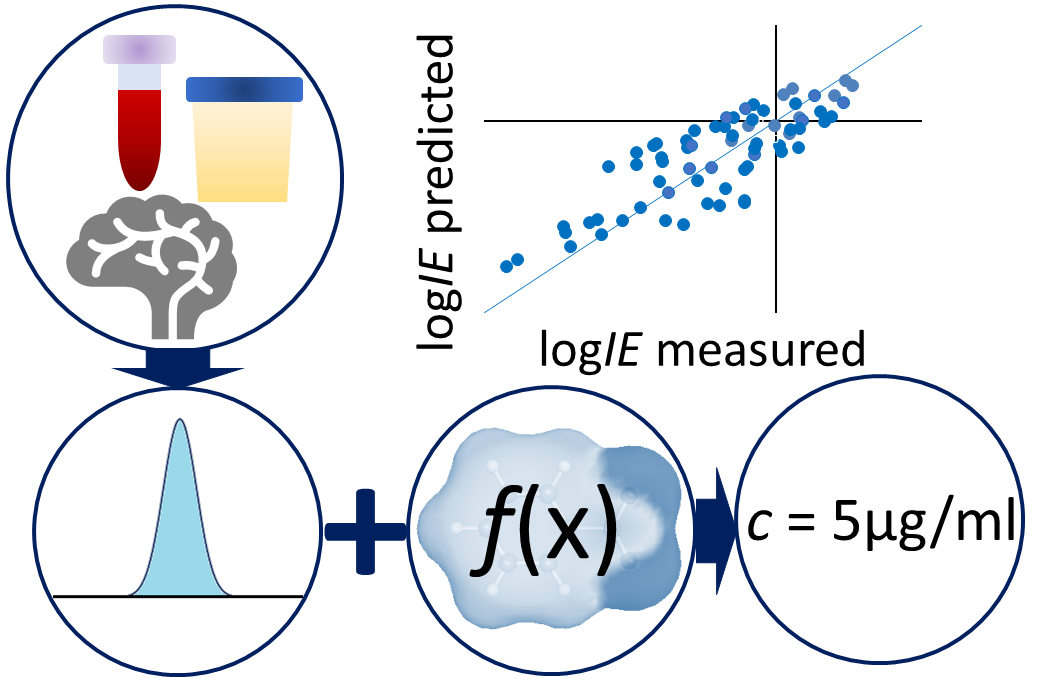
Examining environmental matrix effects on quantitative non-targeted analysis estimates of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances
Shirley Pu, James P McCord, Rebecca A Dickman, Nickolas A Sayresmith, Helen Sepman, Anneli Kruve, Diana S Aga, Jon R Sobus
Anal Bioanal Chem 2023
DOI: 10.1007/s00216-025-05796-1
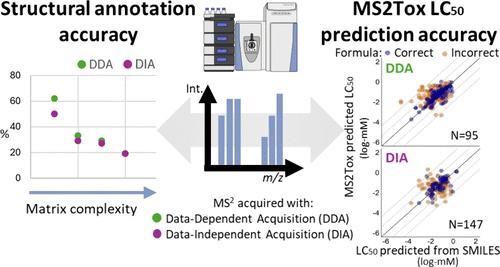
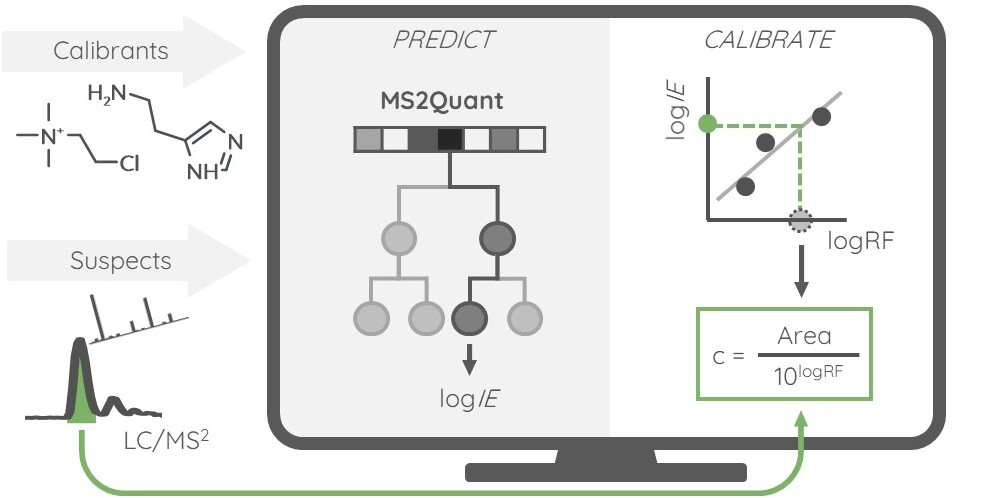
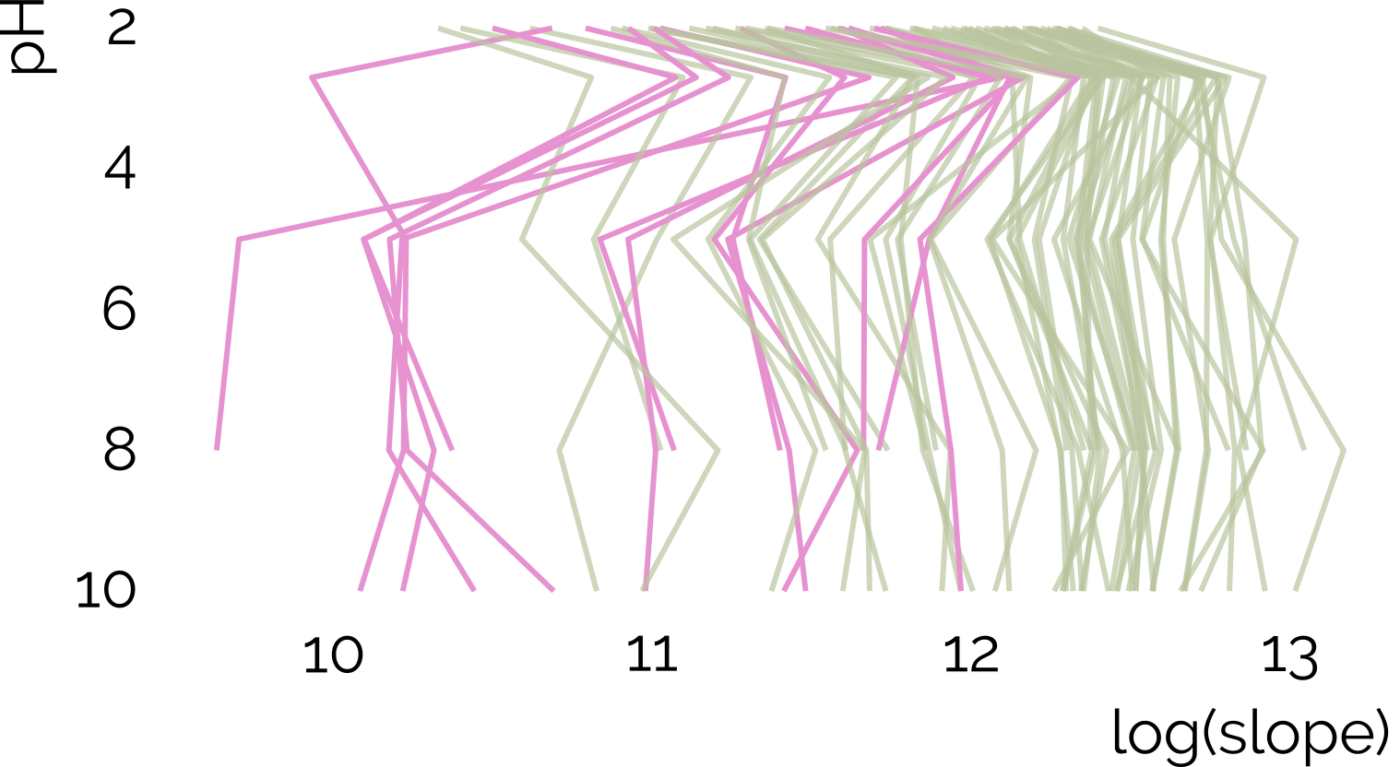
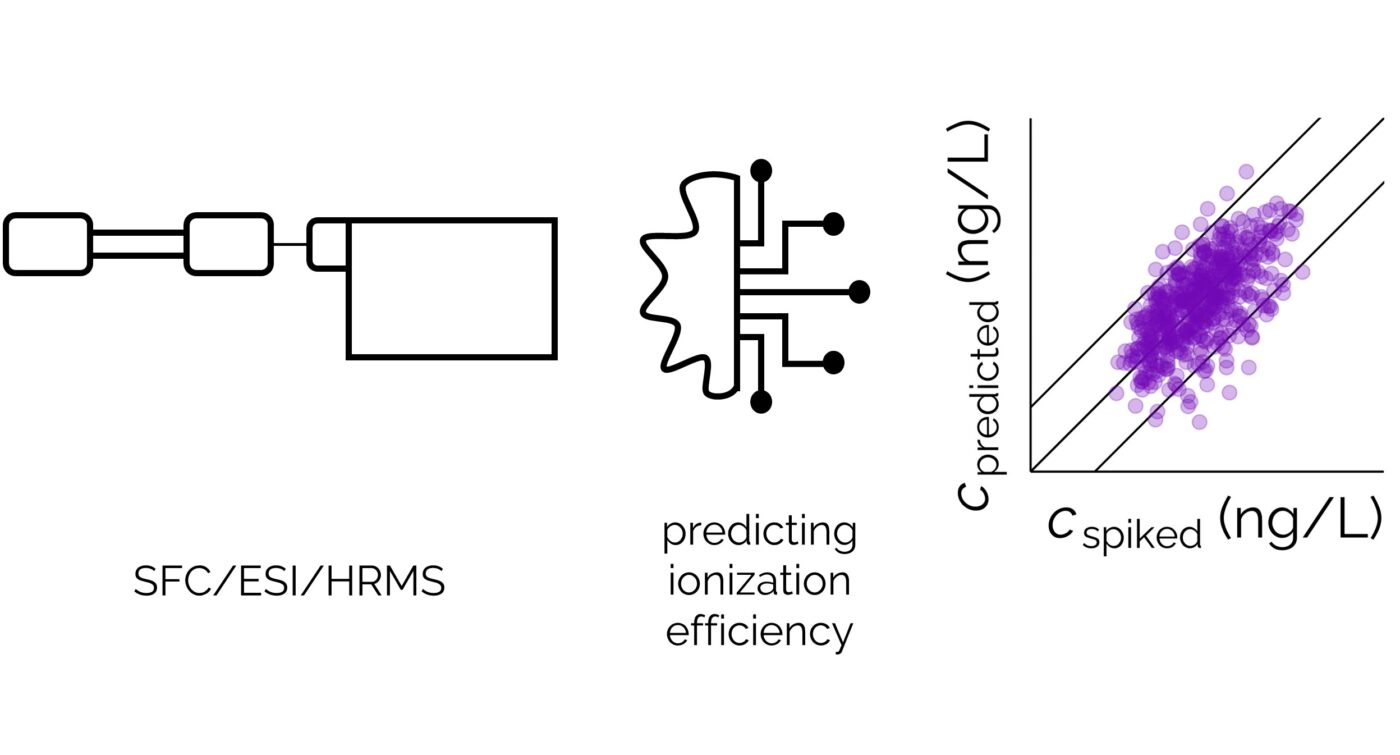
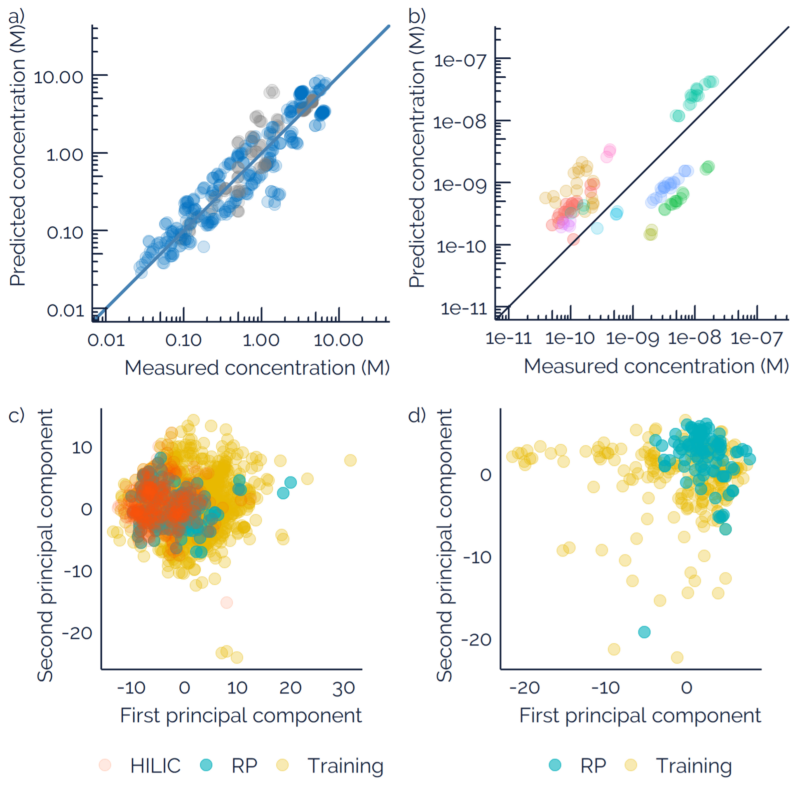
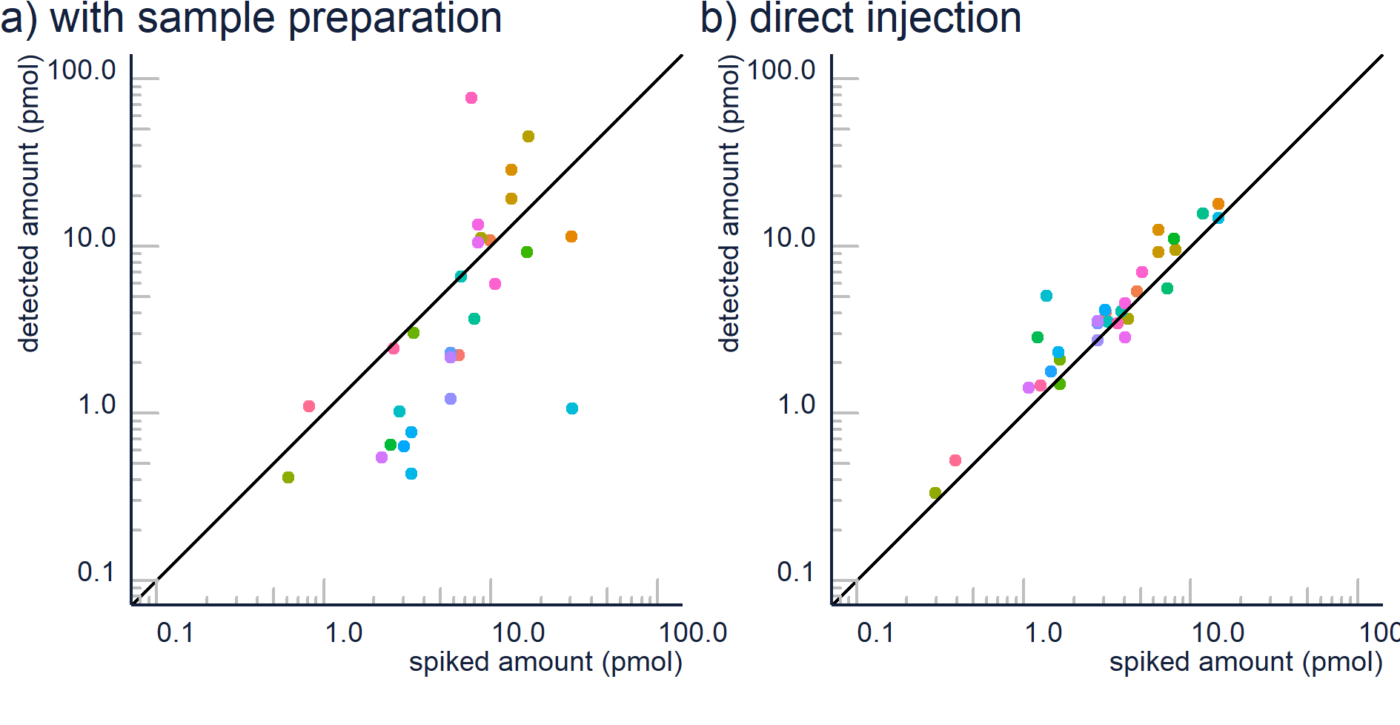
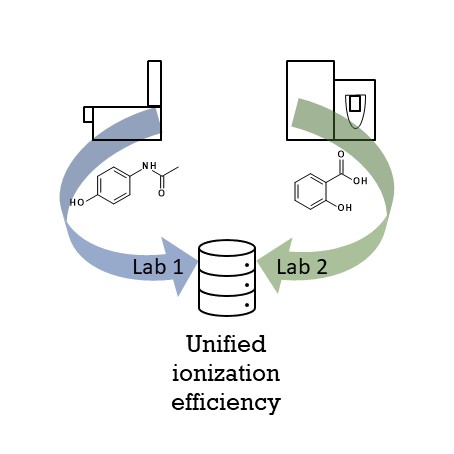
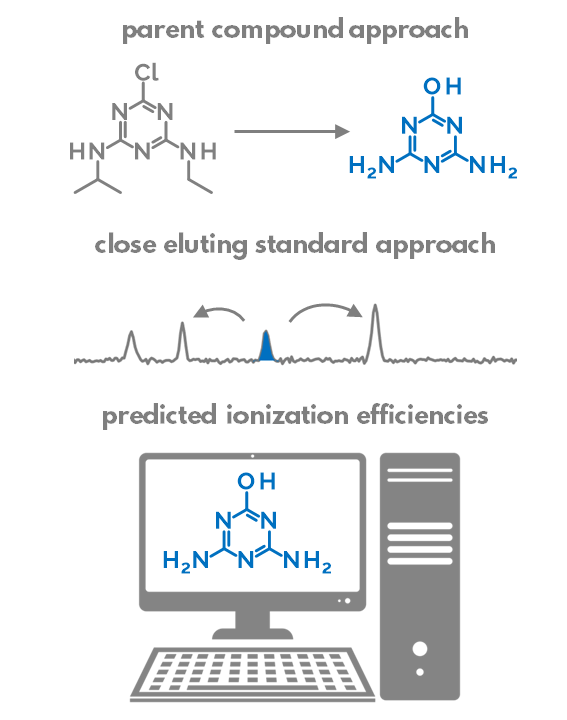
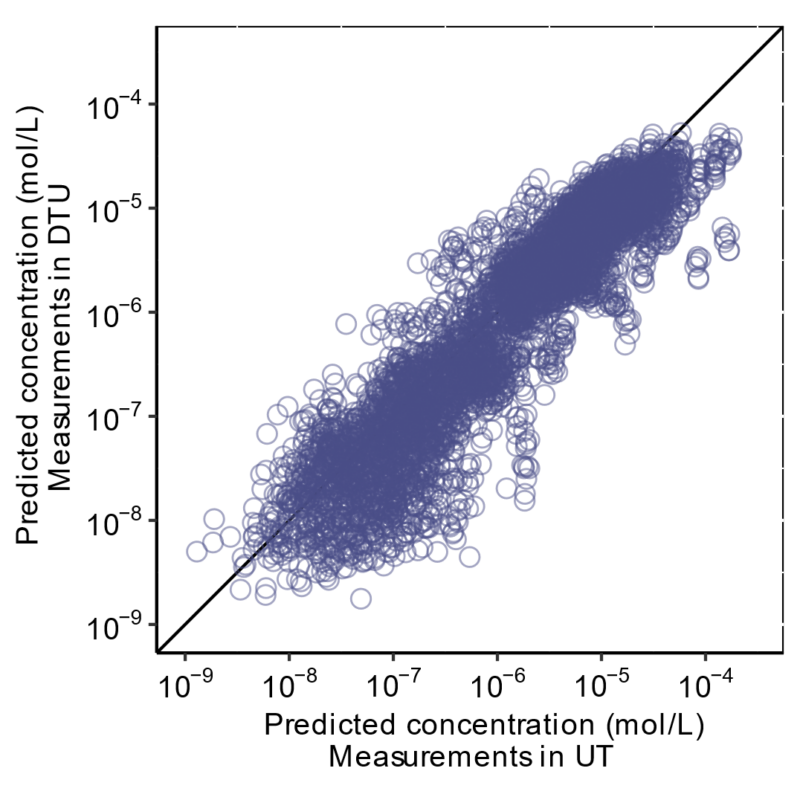
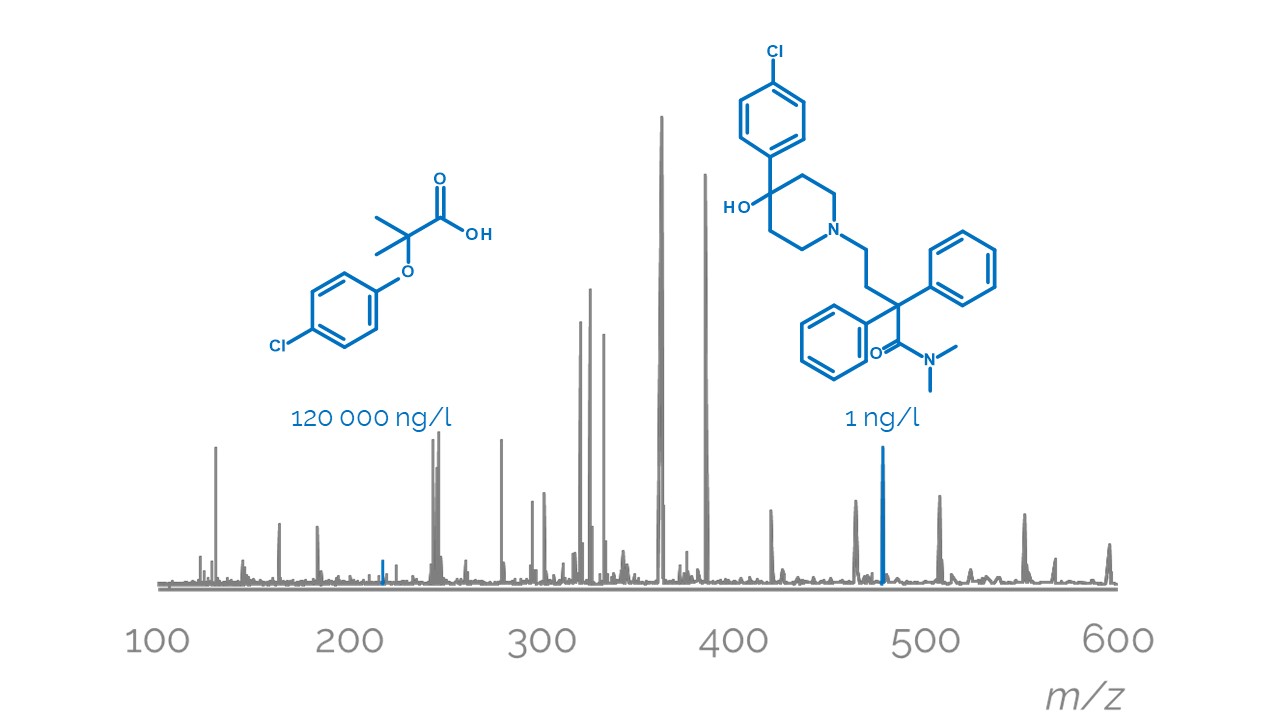
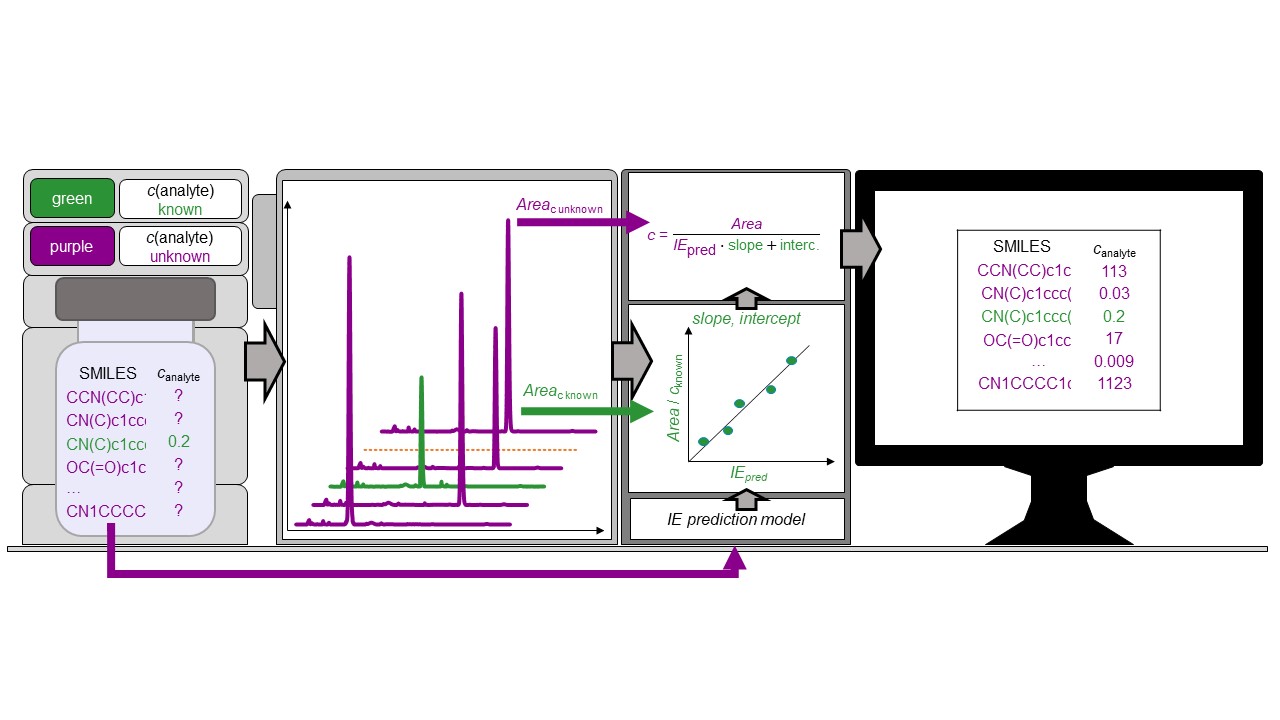
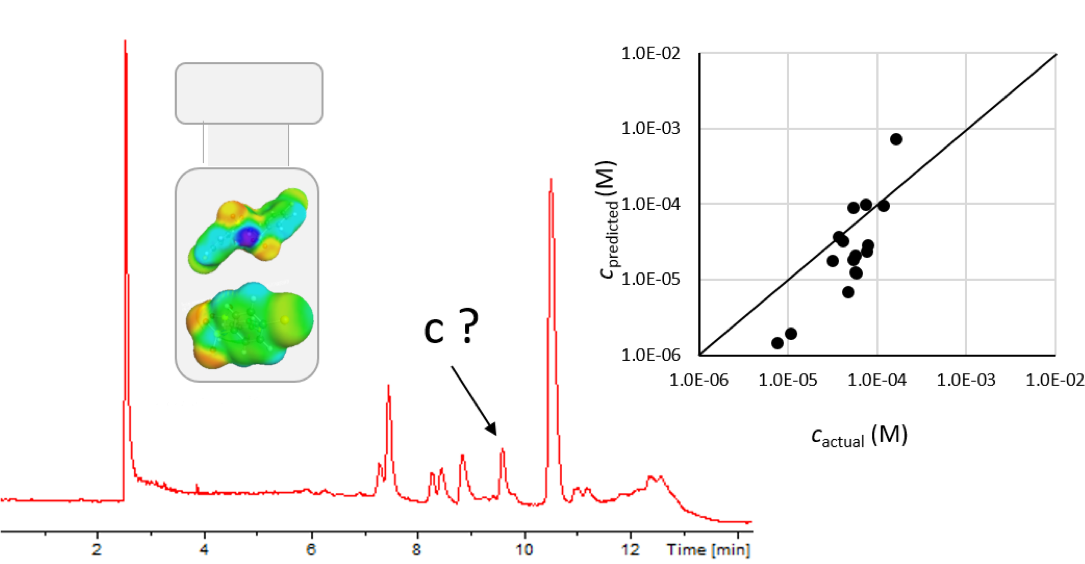
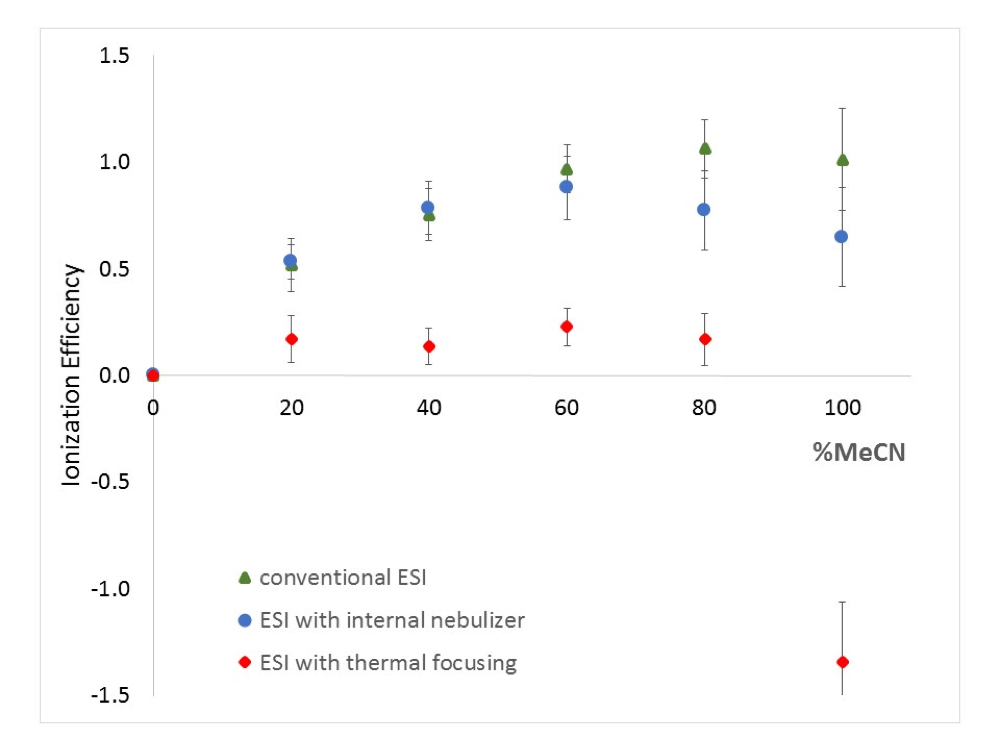
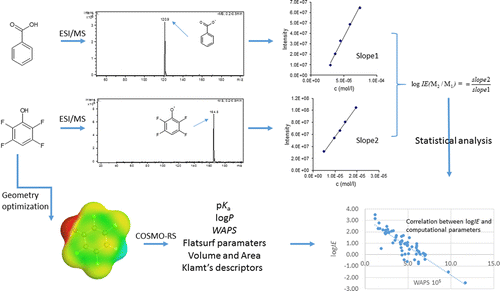
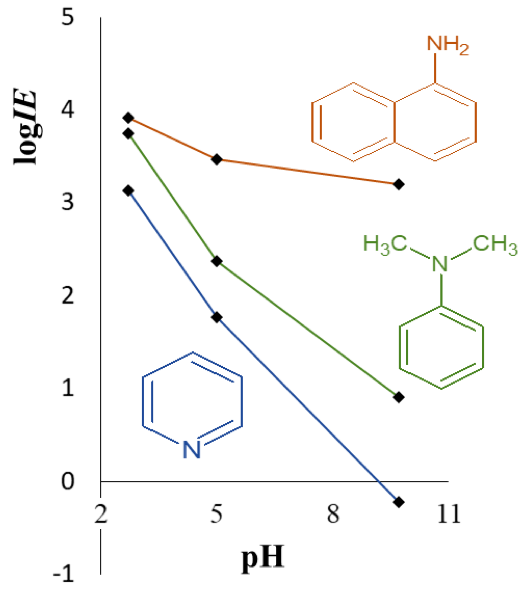
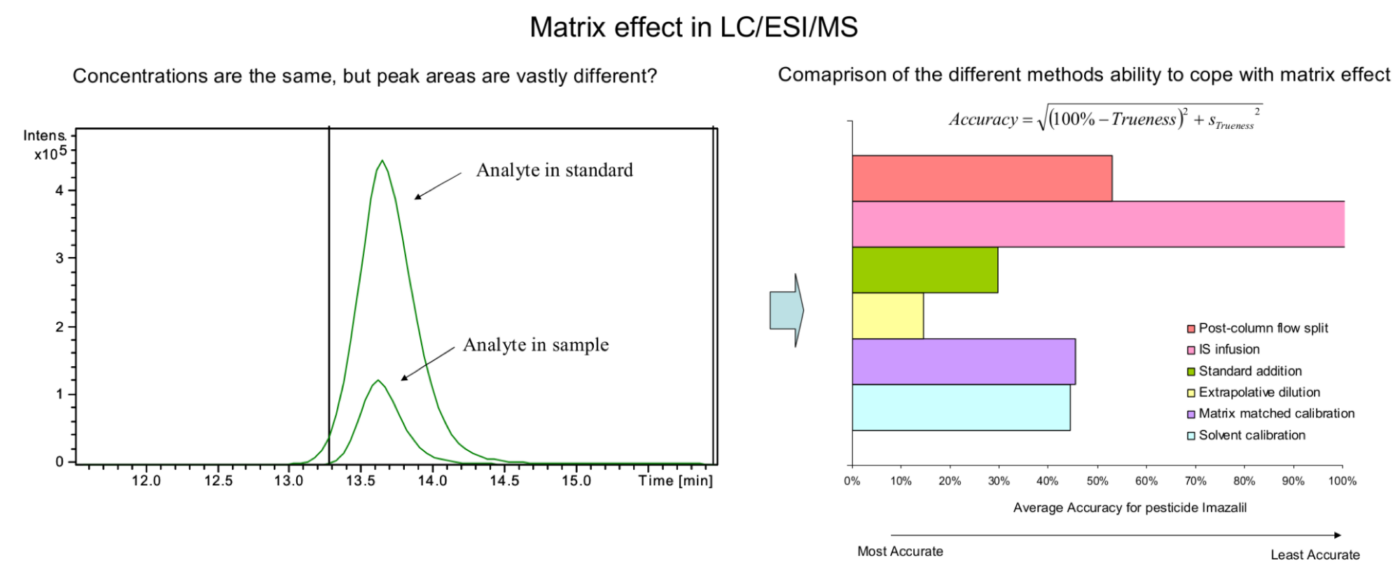
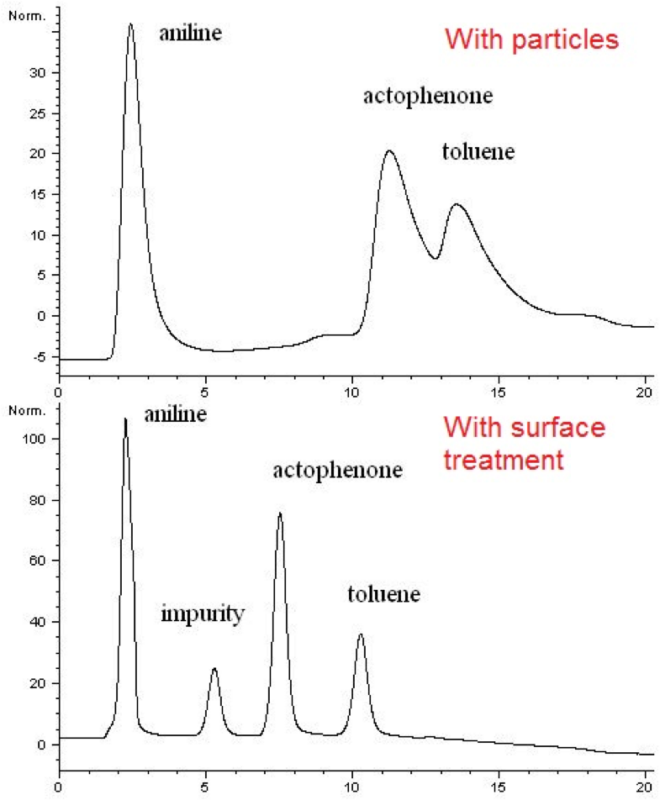
Non-targeted analysis (NTA) is commonly used for the detection and identification of emerging pollutants, including many per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). While NTA outputs are often non-quantitative, concentration estimation is now possible using quantitative non-targeted analysis (qNTA) approaches. To date, few studies have examined matrix effects on qNTA performance, and little is therefore known about the implications of matrix effects on qNTA results and interpretations. Using a set of 19 PFAS, we examined the impacts of drinking water (DW) and waste-activated sludge matrices on qNTA performance across three qNTA approaches: one structure-independent approach based on “global” surrogates and two structure-dependent approaches based on “expert-selected” surrogates and predicted ionization efficiency (IE) regression. The performance of each qNTA approach was examined separately for the PFAS prepared in pure solvent, DW extract, and sludge extract using leave-one-out modeling. Performance was evaluated using previously defined qNTA metrics that describe predictive accuracy, uncertainty, and reliability. The studied sample matrices had minimal effects on qNTA accuracy and larger effects on qNTA uncertainty and reliability. Using solvent-based surrogate data to inform matrix-based estimations yielded lower uncertainty, but also lower reliability, emphasizing that uncertainty must be considered in context of reliability. No single qNTA approach uniformly performed best across all comparisons. Since the IE regression and global surrogates approaches proved most reliable, we recommended them for future qNTA applications. This study highlights the importance of examining multiple performance metrics and utilizing matrix-matched surrogate data in qNTA studies.
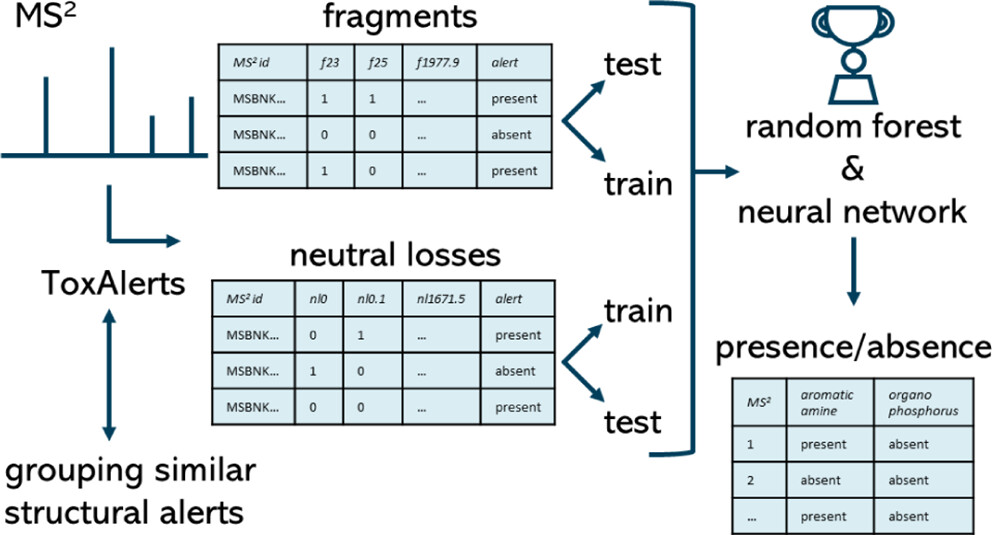
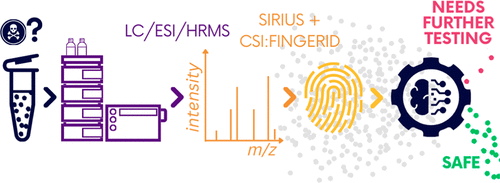
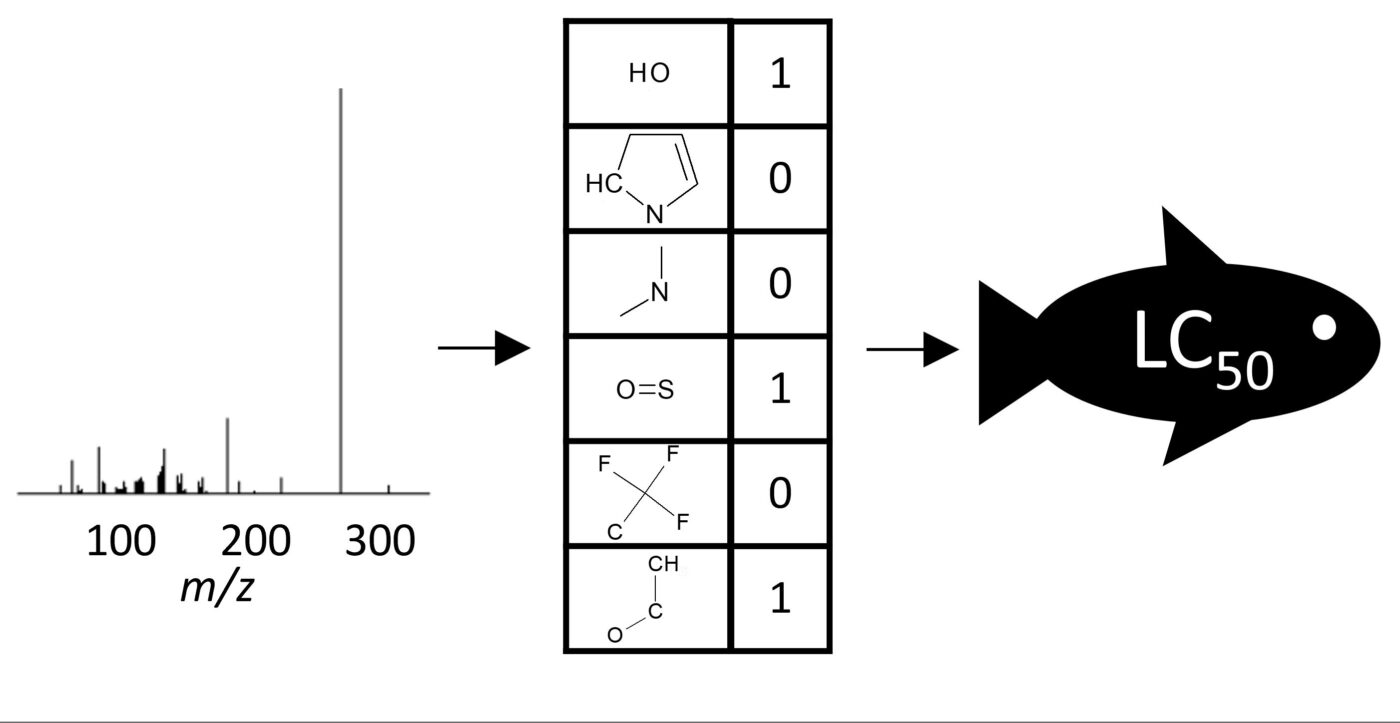
Machine Learning-based Classification for the Prioritization of Potentially Hazardous Chemicals with Structural Alerts in Nontarget Screening
Nienke Meekel, Anneli Kruve, Marja H Lamoree, Frederic M Been
ES&T 2023
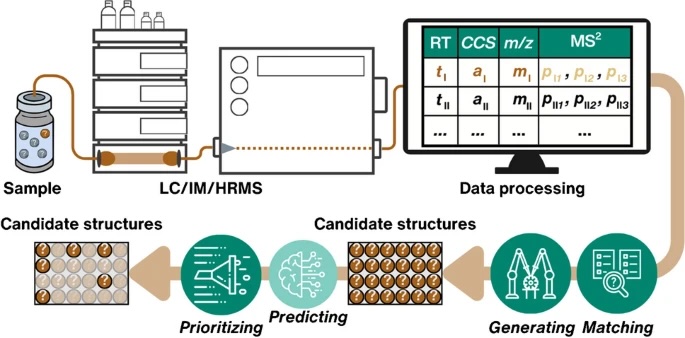
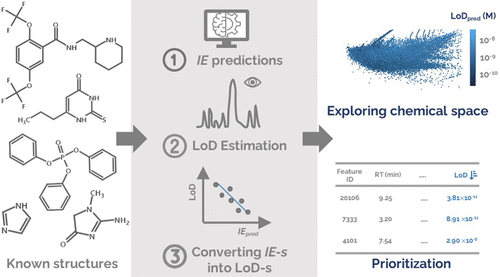
Nontarget screening (NTS) with liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS) is commonly used to detect unknown organic micropollutants in the environment. One of the main challenges in NTS is the prioritization of relevant LC-HRMS features. A novel prioritization strategy based on structural alerts to select NTS features that correspond to potentially hazardous chemicals is presented here. This strategy leverages raw tandem mass spectra (MS2) and machine learning models to predict the probability that NTS features correspond to chemicals with structural alerts. The models were trained on fragments and neutral losses from the experimental MS2 data. The feasibility of this approach is evaluated for two groups: aromatic amines and organophosphorus structural alerts. The neural network classification model for organophosphorus structural alerts achieved an Area Under the Curve of the Receiver Operating Characteristics (AUC-ROC) of 0.97 and a true positive rate of 0.65 on the test set. The random forest model for the classification of aromatic amines achieved an AUC-ROC value of 0.82 and a true positive rate of 0.58 on the test set. The models were successfully applied to prioritize LC-HRMS features in surface water samples, showcasing the high potential to develop and implement this approach further.